Windows 7 accounts that have administrative privileges operate differently than admin accounts in previous versions of the operating system. Rather than giving administrative accounts complete and unbridled access to everything on the PC, these accounts operate as normal user accounts until an action requiring admin privileges pops up. Then the account enters Admin Approval Mode so the user can approve the action.
Much improved over Windows Vista’s handling of admin approval, Windows 7 strikes a balance between security and usability. Fortunately, Microsoft makes it possible to further customize how Admin Approval Mode operates on a PC.
Depending on where your computer is located and who uses it, you can upgrade or downgrade your PC’s security by changing how Windows 7 uses Admin Approval Mode.
Changing How Admin Approval Mode Works
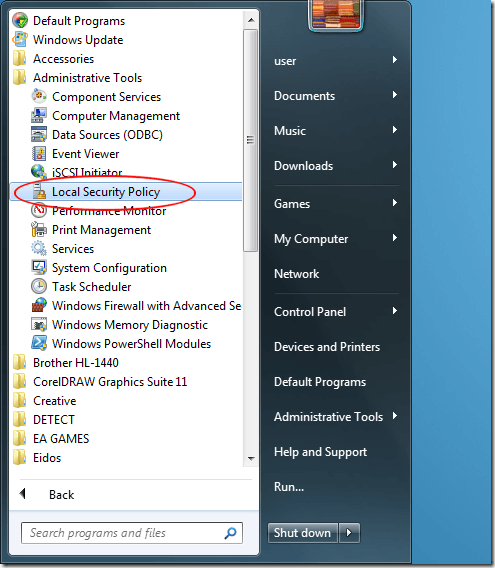
To make changes to how Admin Approval Mode works on a Windows 7 PC, begin by logging into the operating system using an account that has administrative privileges. Click on Start>All Programs>Administrative Tools>Local Security Policy.
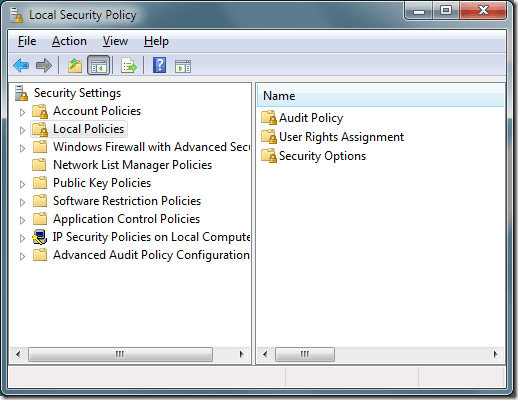
You should now be looking at the Local Security Policy options window.
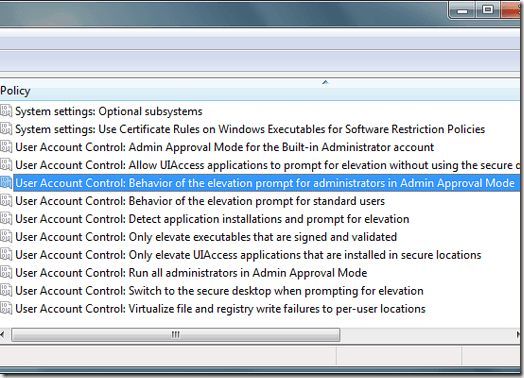
In the left hand pane, click on the folder titled Local Policies and then on the folder labeled Security Options. Locate an option in the right hand pane titled User Account Control: Behavior of the Elevation Prompt for Administrators in Admin Approval Mode. Right click on this option and chooseProperties from the menu.
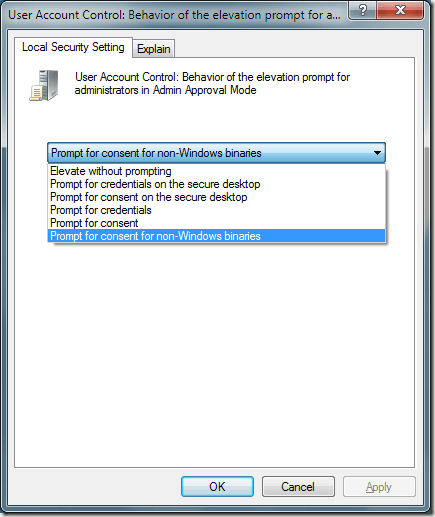
You will notice that you have six options in the drop down menu in the properties window.
Below is a description of each option for Admin Approval Mode elevation.
Six Admin Approval Mode Options
Each of the six Admin Approval Mode Options forces Windows 7 to operate differently when it comes to elevating approval for applications and functions that require approval to run in the operating system.
Elevate Without Prompting
This is the most convenient but also least secure option. Whenever an application or function tries to run that would normally require approval from an administrator, the application or function will run automatically as if it were already given permissions to run. Unless your PC is in a super secure location isolated from networks, this is not a wise choice.
Prompt for Credentials on the Secure Desktop
This option is more secure than the default setting. Whenever an action pops up requiring approval from an admin, Windows 7 will actually prompt the user for a username and password on the secure desktop.
Prompt for Consent on the Secure Desktop
Rather than prompting for a username and password like the option above, Windows 7 will simply ask the user to approve the action on the secure desktop.
Prompt for Credentials
This option operates similarly to the option above titled Prompt for Credentials on the Secure Desktop except that the user types in the username and password without the added security of the secure desktop.
Prompt for Consent
Like the option above titled Prompt for Consent on the Secure Desktop, this option simply asks the user to approve the action but does so without the added security of the secure desktop.
Prompt for Consent for non-Windows Binaries
This is the default Admin Approval Mode option. With this option, users are required to consent to an action only if it requires approval and is not a verified Windows 7 action or executable.
Binaries are simply compiled executable code synonymous to applications or programs. Second only to the Elevate without Prompting option above, this is one of the most liberal Admin Approval Mode options.
Windows 7 strikes a good balance between security and an uninterrupted computing experience but still allows you to further customize how you consent to actions that require admin approval. By altering the Admin Approval Mode options, you can create a customized operating system environment allowing you to increase or decrease security depending on your personal need for administrative security.